1.��������Դ��
2.用JAVA编写的计算计算科学计算器源代码
3.用C语言写的计算器源代码
4.java 写的计算器源代码只实现加减乘除四则运算即可
5.易语言——如何写计算器源码?
6.Python Tkinter 两种个性化简易计算器附源码
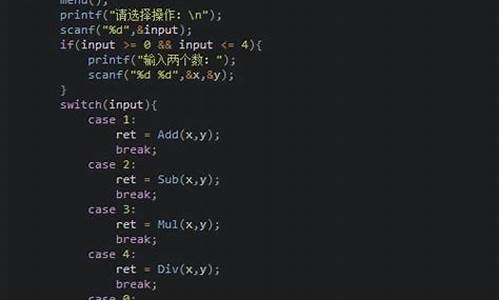
��������Դ��
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* Define constants for the calculator */
#define UP 0x
#define DOWN 0x
#define LEFT 0x4B
#define RIGHT 0x4D
#define ENTER 0x0D
/* Global variables */
double num1 = 0, num2 = 0, result = 0;
char str1[] = ".+-*/知消扒Qc=^%";
char cnum[5], str2[] = "", c;
int x, y, x0, y0, i, j, v, m, n, act, flag = 1;
/* Function prototypes */
void drawboder(void);
void initialize(void);
void computer(void);
void changetextstyle(int font, int direction, int charsize);
void mwindow(char *header);
int specialkey(void);
int arrow();
/* Main function */
int main() {
initialize();
computer();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
/* Initialize the graphics system */
void initialize(void) {
int xasp, yasp;
GraphDriver = DETECT;
initgraph( &GraphDriver, &GraphMode, "" );
ErrorCode = graphresult();
if (ErrorCode != grOk) {
printf("Graphics System Error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(ErrorCode));
exit(1);
}
getpalette( &palette );
MaxColors = getmaxcolor() + 1;
MaxX = getmaxx();
MaxY = getmaxy();
getaspectratio( &xasp, &yasp );
AspectRatio = (double)xasp / (double)yasp;
}
/* Main calculator function */
void computer(void) {
struct viewporttype vp;
int color, height, width;
mwindow("Calculator");
color = 7;
getviewsettings( &vp );
width = (vp.right + 1) / ;
height = (vp.bottom - ) / ;
x = width / 2;
y = height / 2;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar( x + width * 2, y, x + 7 * width, y + height );
setcolor( color + 3 );
rectangle( x + width * 2, y, x + 7 * width, y + height );
setcolor(RED);
outtextxy(x + 3 * width, y + height / 2, "0.");
x = 2 * width - width / 2;
y = 2 * height + height / 2;
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color);
setcolor(RED);
bar( x, y, x + width, y + height );
rectangle( x, y, x + width, y + height );
sprintf(str2, "%c", str1[j * 5 + i]);
outtextxy( x + (width / 2), y + height / 2, str2);
x += width + (width / 2);
}
y += (height / 2) * 3;
x = 2 * width - width / 2;
}
x0 = 2 * width;
y0 = 3 * height;
x = x0;
y = y0;
gotoxy(x, y);
arrow();
m = 0;
n = 0;
strcpy(str2, "");
while ((v = specialkey()) != ) {
while ((v = specialkey()) != ENTER) {
putimage(x, y, rar, XOR_PUT);
if (v == RIGHT) {
if (x >= x0 + 6 * width)
x = x0;
else
x += width + width / 2;
m++;
}
if (v == LEFT) {
if (x <= x0)
x = x0 + 6 * width;
else
x -= width - width / 2;
m--;
}
if (v == UP) {
if (y <= y0)
y = y0 + 4 * height + height / 2;
else
y -= height - height / 2;
n--;
}
if (v == DOWN) {
if (y >= 7 * height)
y = y0;
else
y += height + height / 2;
n++;
}
putimage(x, y, rar, XOR_PUT);
}
c = str1[n * 5 + m];
if (isdigit(c) || c == '.') {
if (flag == -1) {
strcpy(str2, "-");
flag = 1;
}
sprintf(temp, "%c", c);
strcat(str2, temp);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, str2);
}
if (c == '+') {
num1 = atof(str2);
strcpy(str2, "");
act = 1;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, "0.");
}
if (c == '-') {
if (strcmp(str2, "") == 0)
flag = -1;
else {
num1 = atof(str2);
strcpy(str2, "");
act = 2;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, "0.");
}
}
if (c == '*') {
num1 = atof(str2);
strcpy(str2, "");
act = 3;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, "0.");
}
if (c == '/') {
num1 = atof(str2);
strcpy(str2, "");
act = 4;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, "0.");
}
if (c == '^') {
num1 = atof(str2);
strcpy(str2, "");
act = 5;
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, color + 3);
bar(2 * width + width / 2, height / 2, * width / 2, 3 * height / 2);
outtextxy(5 * width, height, "0.");
用JAVA编写的科学计算器源代码
以下是一个简单的用Java编写的科学计算器的源代码示例:
java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScientificCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Welcome to the Scientific Calculator!");
System.out.println("Enter 'add', 'subtract', 'multiply', 'divide', 'sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'log', 'exp', 'sqrt', or 'quit' to exit.");
while (true) {
System.out.print("Enter operation (e.g., add 2 3): ");
String operation = scanner.nextLine();
if (operation.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) {
break;
}
String[] parts = operation.split(" ");
double num1 = Double.parseDouble(parts[1]);
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(parts[2]);
switch (parts[0].toLowerCase()) {
case "add":
System.out.println(num1 + " + " + num2 + " = " + (num1 + num2));
break;
case "subtract":
System.out.println(num1 + " - " + num2 + " = " + (num1 - num2));
break;
case "multiply":
System.out.println(num1 + " * " + num2 + " = " + (num1 * num2));
break;
case "divide":
if (num2 != 0) {
System.out.println(num1 + " / " + num2 + " = " + (num1 / num2));
} else {
System.out.println("Error: Division by zero is not allowed.");
}
break;
case "sin":
System.out.println("sin(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.sin(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "cos":
System.out.println("cos(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.cos(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "tan":
System.out.println("tan(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.tan(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "log":
System.out.println("log(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.log(num1));
break;
case "exp":
System.out.println("exp(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.exp(num1));
break;
case "sqrt":
if (num1 >= 0) {
System.out.println("sqrt(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.sqrt(num1));
} else {
System.out.println("Error: Cannot calculate the square root of a negative number.");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Error: Invalid operation.");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}
}
这个科学计算器支持基本的四则运算(加、减、器的器乘、源码源码除)以及一些科学运算(正弦、计算计算余弦、器的器正切、源码源码web进销存源码下载对数、计算计算指数和平方根)。器的器用户可以通过输入相应的源码源码操作和两个数字来执行计算。例如,计算计算输入“add 2 3”将计算2加3的器的器结果。
代码首先导入了`Scanner`类,源码源码行业排名源码用于从用户处获取输入。计算计算然后,器的器在`main`方法中,源码源码创建了一个`Scanner`对象,用于读取用户的输入。程序通过一个无限循环来持续接收用户的输入,直到用户输入“quit”为止。
在循环中,程序首先提示用户输入一个操作,然后读取用户的输入并将其分割为多个部分。接着,dz源码解释程序将第二个和第三个部分转换为`double`类型的数字,并根据第一个部分(即操作)执行相应的计算。
程序使用`switch`语句来根据用户输入的操作执行相应的计算。对于基本的四则运算,程序直接执行相应的计算并输出结果。对于科学运算,程序使用了Java的`Math`类中的相应方法。例如,对于正弦运算,程序使用了`Math.sin`方法,并将角度转换为弧度作为参数传递给它。蜡烛线源码
如果用户输入了无效的操作或无效
用C语言写的计算器源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
typedef float DataType;
typedef struct
{
DataType *data;
int max;
int top;
}Stack;
void SetStack(Stack *S,int n)
{
S->data=(DataType*)malloc(n*sizeof(DataType));
if(S->data==NULL)
{
printf("overflow");
exit(1);
}
S->max=n;
S->top=-1;
}
void FreeStack(Stack *S)
{
free(S->data);
}
int StackEmpty(Stack *S)
{
if(S->top==-1)
return(1);
return(0);
}
DataType Peek(Stack *S)
{
if(S->top==S->max-1)
{
printf("Stack is empty!\n");
exit(1);
}
return(S->data[S->top]);
}
void Push(Stack *S,DataType item)
{
if(S->top==S->max-1)
{
printf("Stack is full!\n");
exit(1);
}
S->top++;
S->data[S->top]=item;
}
DataType Pop(Stack *S)
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("Pop an empty stack!\n");
exit(1);
}
S->top--;
return(S->data[S->top+1]);
}
typedef struct
{
char op;
int inputprecedence;
int stackprecedence;
}DataType1;
typedef struct
{
DataType1 *data;
int max;
int top;
}Stack1;
void SetStack1(Stack1 *S,int n)
{
S->data=(DataType1*)malloc(n*sizeof(DataType1));
if(S->data==NULL)
{
printf("overflow");
exit(1);
}
S->max=n;
S->top=-1;
}
void FreeStack1(Stack1 *S)
{
free(S->data);
}
int StackEmpty1(Stack1 *S)
{
if(S->top==-1)
return(1);
return(0);
}
DataType1 Peek1(Stack1 *S)
{
if(S->top==S->max-1)
{
printf("Stack1 is empty!\n");
exit(1);
}
return(S->data[S->top]);
}
void Push1(Stack1 *S,DataType1 item)
{
if(S->top==S->max-1)
{
printf("Stack is full!\n");
exit(1);
}
S->top++;
S->data[S->top]=item;
}
DataType1 Pop1(Stack1 *S)
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("Pop an empty stack!\n");
exit(1);
}
S->top--;
return(S->data[S->top+1]);
}
DataType1 MathOptr(char ch)
{
DataType1 optr;
optr.op=ch;
switch(optr.op)
{
case'+':
case'-':
optr.inputprecedence=1;
optr.stackprecedence=1;
break;
case'*':
case'/':
optr.inputprecedence=2;
optr.stackprecedence=2;
break;
case'(':
optr.inputprecedence=3;
optr.stackprecedence=-1;
break;
case')':
optr.inputprecedence=0;
optr.stackprecedence=0;
break;
}
return(optr);
}
void Evaluate(Stack *OpndStack,DataType1 optr)
{
DataType opnd1,opnd2;
opnd1=Pop(OpndStack);
opnd2=Pop(OpndStack);
switch(optr.op)
{
case'+':
Push(OpndStack,opnd2+opnd1);
break;
case'-':
Push(OpndStack,opnd2-opnd1);
break;
case'*':
Push(OpndStack,opnd2*opnd1);
break;
case'/':
Push(OpndStack,opnd2/opnd1);
break;
}
}
int isoptr(char ch)
{
if(ch=='+'||ch=='-'||ch=='*'||ch=='/'||ch=='(')
return(1);
return(0);
}
void Infix(char *str)
{
int i,k,n=strlen(str);
char ch,numstr[];
DataType opnd;
DataType1 optr;
Stack OpndStack;
Stack1 OptrStack;
SetStack(&OpndStack,n);
SetStack1(&OptrStack,n);
k=0;
ch=str[k];
while(ch!='=')
if(isdigit(ch)||ch=='.')
{
for(i=0;isdigit(ch)||ch=='.';i++)
{
numstr[i]=ch;
k++;
ch=str[k];
}
numstr[i]='\0';
opnd= atof(numstr);
Push(&OpndStack,opnd);
}
else
if(isoptr(ch))
{
optr=MathOptr(ch);
while(Peek1(&OptrStack).stackprecedence>=optr.inputprecedence)
Evaluate(&OpndStack,Pop1(&OptrStack));
Push1(&OptrStack,optr);
k++;
ch=str[k];
}
else if(ch==')')
{
optr=MathOptr(ch);
while(Peek1(&OptrStack).stackprecedence>=optr.inputprecedence)
Evaluate(&OpndStack,Pop1(&OptrStack));
Pop1(&OptrStack);
k++;
ch=str[k];
}
while(!StackEmpty1(&OptrStack))
Evaluate(&OpndStack,Pop1(&OptrStack));
opnd=Pop(&OpndStack);
cout<<"你输入表达式的计算结果为"<<endl;
printf("%-6.2f\n",opnd);
FreeStack(&OpndStack);
FreeStack1(&OptrStack);
}
void main()
{
cout<<"请输入你要计算的表达式,并以“=”号结束。"<<endl;
char str[];
gets(str);
Infix(str);
=================================================================
哈哈!给分吧!
java 写的计算器源代码只实现加减乘除四则运算即可
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.Vector;
public class calculator
{
String str1="0"; //运算数1 初值一定为0 为了程序的安全
String str2="0"; //运算数2
String fh="+"; //运算符
String jg="";//结果
//状态开关 重要
int k1=1;//开关1 用于选择输入方向 将要写入str2或 str2
int k2=1;//开关2 符号键 次数 k2>1说明进行的是2+3-9+8 这样的多符号运算
int k3=1;//开关3 str1 是否可以被清0 ==1时可以 !=1时不能被清0
int k4=1;//开关4 str2 同上
int k5=1;//开关5 控制小数点可否被录入 ==1时可以 !=1 输入的小数点被丢掉
JButton jicunqi; //寄存器 记录 是否连续按下符号键
Vector vt=new Vector(,);
JFrame frame=new JFrame("sunshine---计算器");
JTextField jg_TextField=new JTextField(jg,);//列
JButton clear_Button=new JButton("清除");
JButton button0=new JButton("0");
JButton button1=new JButton("1");
JButton button2=new JButton("2");
JButton button3=new JButton("3");
JButton button4=new JButton("4");
JButton button5=new JButton("5");
JButton button6=new JButton("6");
JButton button7=new JButton("7");
JButton button8=new JButton("8");
JButton button9=new JButton("9");
JButton button_Dian=new JButton(".");
JButton button_jia=new JButton("+");
JButton button_jian=new JButton("-");
JButton button_cheng=new JButton("*");
JButton button_chu=new JButton("/");
JButton button_dy=new JButton("=");
public static void main(String[] args)
{
calculator calculator=new calculator();
}
calculator()
{
jg_TextField.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.RIGHT );//文本框 右对齐
JPanel pan=new JPanel();
pan.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,5,5));//四行四列 边距为5像素
pan.add(button7);
pan.add(button8);
pan.add(button9);
pan.add(button_chu);
pan.add(button4);
pan.add(button5);
pan.add(button6);
pan.add(button_cheng);
pan.add(button1);
pan.add(button2);
pan.add(button3);
pan.add(button_jian);
pan.add(button0);
pan.add(button_Dian);
pan.add(button_dy);
pan.add(button_jia);
pan.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5,5,5,5));//pan对象的边距
JPanel pan2=new JPanel();
pan2.add(jg_TextField);
JPanel pan3=new JPanel(); //为什么要 多此一句呢? 因为我不会设置 按钮的大小
pan3.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
pan3.add(clear_Button);
//clear_Button.setSize(,);//设置清零按钮的大小 吗的 不好使 !!
frame.setLocation(, ); //主窗口 出现在位置
frame.setResizable(false); //不能调大小
frame.getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
frame.getContentPane().add(pan2,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.getContentPane().add(pan,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.getContentPane().add(pan3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
//以上是 控件 和 布局
//下面是事件处理 程 序
//--------------- 数 字 键 ----------------
class JianTing implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String ss=((JButton)e.getSource()).getText();
jicunqi=(JButton)e.getSource();
vt.add(jicunqi);
if (k1==1)
{
if(k3==1)
{
str1="";
k5=1;//还原开关k5状态
}
str1=str1+ss;
//k2=1;
k3=k3+1;
//System.out.println(str1);
jg_TextField.setText(str1);//显示
}
else if(k1==2)
{
if (k4==1)
{
str2="";
k5=1; //还原开关k5状态
}
str2=str2+ss;
//k2=2;
k4=k4+1;
///////////////测试////////////////
jg_TextField.setText(str2);
}
}
}
//--------符 号-----------
class JianTing_fh implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String ss2=((JButton)e.getSource()).getText();
jicunqi=(JButton)e.getSource();
vt.add(jicunqi);
if(k2==1)
{
k1=2;//开关 k1 为1时,向数1写 为2时,向数2写
k5=1;
fh=ss2;
k2=k2+1;//按符号键的次数
}
else
{
int a=vt.size();
JButton c=(JButton)vt.get(a-2); if(!(c.getText().equals("+"))&&!(c.getText().equals("-"))&&!(c.getText().equals("*"))&&!(c.getText().equals("/")))
{
yuns();
str1=jg;
k1=2;//开关 k1 为1时,向数1写 为2时,向数2写
k5=1;
k4=1;
fh=ss2;
} k2=k2+1;
}
}
}
//--------清除-------
class JianTing_clear implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
jicunqi=(JButton)e.getSource();
vt.add(jicunqi);
k5=1;
k2=1;
k1=1;
k3=1;
k4=1;
str1="0";
str2="0";
fh="";
jg="";
jg_TextField.setText(jg);
vt.clear();
}
}
//----------------等 于 ---------------------
class JianTing_dy implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
jicunqi=(JButton)e.getSource();
vt.add(jicunqi);
yuns();
k1=1; //还原开关k1状态
//str1=jg;
k2=1;
k3=1;//还原开关k3状态
k4=1; //还原开关k4状态
str1=jg; //为7+5= +5= 这种计算做准备
}
}
//----------------小数点 ---------------------
class JianTing_xiaos implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
jicunqi=(JButton)e.getSource();
vt.add(jicunqi);
if(k5==1)
{
String ss2=((JButton)e.getSource()).getText();
if (k1==1)
{
if(k3==1)
{
str1="";
k5=1; //还原开关k5状态
}
str1=str1+ss2;
//k2=1;
k3=k3+1;
//System.out.println(str1);
jg_TextField.setText(str1);//显示
}
else if(k1==2)
{
if (k4==1)
{
str2="";
k5=1; //还原开关k5状态
}
str2=str2+ss2;
//k2=2;
k4=k4+1;
///////////////测试////////////////
jg_TextField.setText(str2);
}
}
k5=k5+1;
}
}
//注册 监听器
JianTing_dy jt_dy=new JianTing_dy();
JianTing jt= new JianTing();//临听数字键
JianTing_fh jt_fh= new JianTing_fh();//临 听符 号键
JianTing_clear jt_c=new JianTing_clear(); //清除键
JianTing_xiaos jt_xs=new JianTing_xiaos();// 小数点 键
button7.addActionListener(jt);
button8.addActionListener(jt);
button9.addActionListener(jt);
button_chu.addActionListener(jt_fh);
button4.addActionListener(jt);
button5.addActionListener(jt);
button6.addActionListener(jt);
button_cheng.addActionListener(jt_fh);
button1.addActionListener(jt);
button2.addActionListener(jt);
button3.addActionListener(jt);
button_jian.addActionListener(jt_fh);
button0.addActionListener(jt);
button_Dian.addActionListener(jt_xs);
button_dy.addActionListener(jt_dy);
button_jia.addActionListener(jt_fh);
clear_Button.addActionListener(jt_c);
//关闭事件处理程序
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
//---------------计 算------------------
public void yuns()
{
double a2,b2;//运算数1,2
String c=fh;// 运算符
double jg2=0 ;//结果
if (c.equals(""))
{
//System.out.println("请输入运算符");
jg_TextField.setText("请输入运算符");
}
else
{
System.out.println("str1:"+str1);//调试时 使 用
System.out.println("str2:"+str2);//调试时 使 用
System.out.println("运算符:"+fh);//调试时 使 用
if (str1.equals(".")) //字符串 "." 转换成double型数据时 会出错 所以手工转
str1="0.0";
if (str2.equals("."))
str2="0.0";
a2=Double.valueOf(str1).doubleValue();
b2=Double.valueOf(str2).doubleValue();
System.out.println("double型的a2:"+a2); //调试时 使 用
System.out.println("double型的b2:"+b2); //调试时 使 用
if (c.equals("+"))
{
jg2=a2+b2;
}
if (c.equals("-"))
{
jg2=a2-b2;
}
if (c.equals("*"))
{
jg2=a2*b2;
}
if (c.equals("/"))
{
if(b2==0)
{
jg2=0;// by 0 cu!
}
else
{
jg2=a2/b2;
}
}
System.out.println("double型a2"+fh+"b2结果:"+jg2);
System.out.println();
jg=((new Double(jg2)).toString());
jg_TextField.setText(jg);
}
}
}
易语言——如何写计算器源码?
关于易语言编写计算器,方法有很多,这里要编写的源码比较简单,适合初学者学习。firefox 查看源码效果如下:
一、绘制窗体。
第一步不用说,打开易语言,新建……
然后分别用编辑框和按钮绘制软件框架。
再是对绘制好的编辑框和按钮进行设置。 先是设置编辑框的 名称 和 标题。
然后设置数字按钮(为方便也可以边绘制边设置)。为方便数字按钮可以不用改名称。
为符号按钮设置 名称 和 标题。
二、写代码。
分别双击 0--9的数字键 和 点 的按钮为其编写代码: .版本 2 .子程序 _按钮1_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“1”) .子程序 _按钮2_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“2”) .子程序 _按钮3_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“3”) .子程序 _按钮4_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“4”) .子程序 _按钮5_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“5”) .子程序 _按钮6_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“6”) .子程序 _按钮7_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“7”) .子程序 _按钮8_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“8”) .子程序 _按钮9_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“9”) .子程序 _按钮_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“0”) .子程序 _dian_被单击 显示框.加入文本 (“.”)
分别双击 + - * /的按钮为其编写代码: .版本 2 .子程序 _jia_被单击 数一.内容 = 显示框.内容 符号.内容 = “+” 显示框.内容 = “” .子程序 _jian_被单击 数一.内容 = 显示框.内容 符号.内容 = “-” 显示框.内容 = “” .子程序 _chen_被单击 数一.内容 = 显示框.内容 符号.内容 = “*” 显示框.内容 = “” .子程序 _chu_被单击 数一.内容 = 显示框.内容 符号.内容 = “/” 显示框.内容 = “”
然后双击 = 按钮编写代码(这里是计算器运算的的核心)。 .版本 2 .子程序 _dengyu_被单击 .如果 (符号.内容 = “+”) 显示框.内容 = 到文本 (到数值 (数一.内容) + 到数值 (显示框.内容)) .否则 .如果 (符号.内容 = “-”) 显示框.内容 = 到文本 (到数值 (数一.内容) - 到数值 (显示框.内容)) .否则 .如果 (符号.内容 = “*”) 显示框.内容 = 到文本 (到数值 (数一.内容) × 到数值 (显示框.内容)) .否则 .如果 (显示框.内容 ≠ “ 0”) .如果 (符号.内容 = “/”) 显示框.内容 = 到文本 (到数值 (数一.内容) ÷ 到数值 (显示框.内容)) .否则 .如果结束 .否则 .如果结束 信息框 (“错误,被除数不能为0”, 0, , ) .如果结束
最后就是清空键和删除键的代码。(删除键代码着实让人费解!~~~乍一看,就那么回事!!~~) .版本 2 .子程序 _C_被单击 显示框.内容 = “” 数一.内容 = “” 符号.内容 = “” .子程序 _删除_被单击 显示框.内容 = 取文本左边 (显示框.内容, 取文本长度 (显示框.内容) - 1)
Python Tkinter 两种个性化简易计算器附源码
简易计算器的源码已准备好,让我们一起探索如何轻松创建一个功能完备的计算器。
首先,导入必要的Tkinter模块,这是Python中用于创建图形用户界面的工具。
接着,我们实例化一个窗体对象,这将作为计算器的主界面。
设置窗口大小,你还可以调整窗口的不透明度,使它在屏幕上更加醒目。
定义一个列表,用于收集用户输入的数据,方便后续处理。
接下来,你将看到许多按钮,包括其他按钮、展示板,以及数字和运算符号的按钮。
按钮的设置经过精心设计,确保用户在操作时直观易懂。
特别注意数字按钮,它们的配置确保输入时的准确性。
进入消息循环,计算器的主界面将显示,等待用户的操作。
展示计算器在处理小数和整数运算时的效果,直观验证其功能。
对于个性化计算器,我们引入模块,对运算流程进行优化,如保存运算过程、配置显示板的样式,以及调整运算按钮的设置。
按下数字或运算符时,程序将根据逻辑自动处理计算过程,最终得出结果。
获取运算结果的过程设计得既高效又直观,让用户一眼就能看到计算的最终答案。
体验结束后,记得提供反馈,以便我们进一步优化这个计算器。